MARINE
SHAFT POWER METERS
MARINE OVERVIEW
Binsfeld Engineering is proud to be a market-leader in the marine market, offering user-friendly and easily integrated torque and power measurement solutions. Whether our customers want to monitor vessel performance, diagnose the root cause of repeated component failures, or increase fuel efficiency, Binsfeld shaft power meters provide the data needed to get the job done.
PERFORMANCE MONITORING
- Reduce downtime by knowing when engine, propeller, gearbox, or bearing performance is degrading
- Initiate preventative maintenance or replace worn components only when needed
DIAGNOSTICS/TESTING
- Diagnose propulsion problems
- Figure out why hull efficiency has degraded (hull-fouling)
- Determine the root cause of an excessive torsional vibration on a propeller shaft
OPTIMIZE FUEL EFFICIENCY & REDUCE EMISSIONS
- Combine mechanical horsepower measurement with vessel speed and fuel consumption sensors to monitor fuel consumption and increase fuel efficiency
- Meet emissions requirements by optimizing fuel efficiency

MARINE PRODUCTS & SERVICES
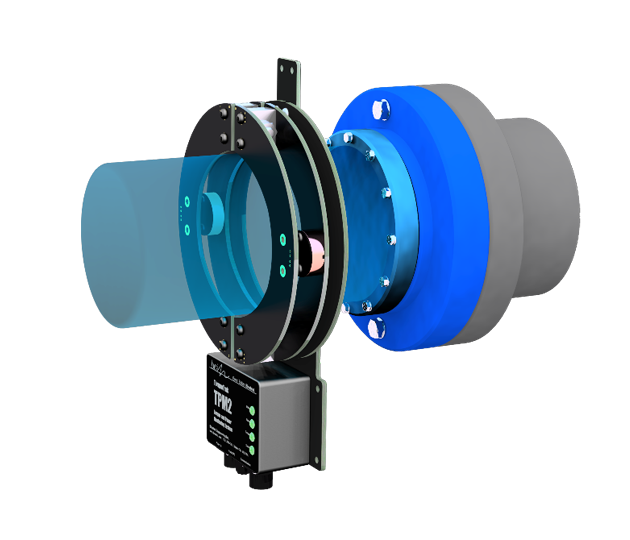
TPM2 SHAFT POWER METER
Digital system used for vessel shaft torque and power measurements. Sealed (IP-67), Vibration (MIL-STD-167-1A), & Shock-Tested (MIL-STD-810H).
TorqueTrak SPM-iON
A state-of-the-art strain gage-based solution designed to provide torque, RPM, and power measurements on rotating shafts, without the need for shaft disassembly or modification.
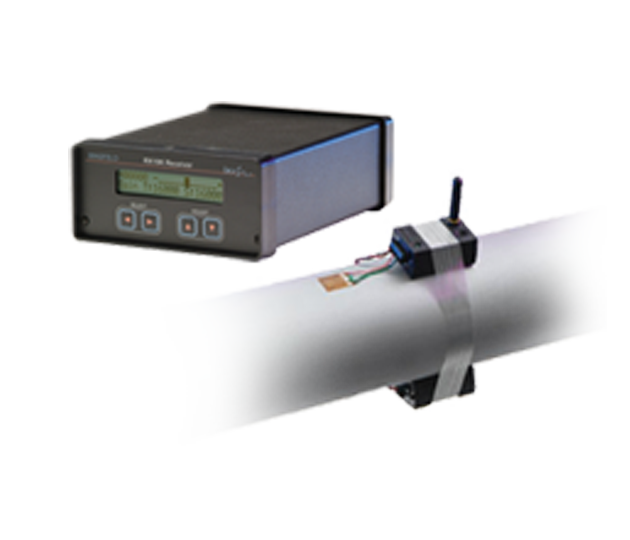
SEA TRIAL KIT
Portable measurement system used for sea trials, horsepower verification, and torsional vibration measurements.
MARINE CLIENTS





EDISON CHOUEST OFFSHORE
ROLLS-ROYCE MARINE
BOLLINGER SHIPYARDS
CANADIAN COAST GUARD
GROUPE OCÉAN
ADDITIONAL MARINE CASE STUDIES
Marine Propulsion System Upgrade Trials
LamaLo Technology Inc. (LLT) commonly conducts marine propulsion shafting vibration and powering measurements in support of new construction, propulsion upgrades, and troubleshooting. Binsfeld TorqueTrak 10K telemetry systems are used to measure the shaft torque....
‘Ghost’ Torque Captured Onboard Navy Ship
Rolls-Royce Marine NA in Old Saybrook, Connecticut was asked by the US Navy to investigate a report of rudder post binding on one of their ships. Although none of the affected equipment was manufactured by Rolls-Royce, the Navy sought the Marine Engineering Services...
Ship Propulsion System: Navy Relies on Telemetry for Sea Trials
Transfield Defence Systems, Melbourne, Australia - Catastrophic failure of the port drive shaft on the Australian naval frigate, HMAS Anzac, led to expensive dry-dock repairs. Potential variations in the newly installed drive system could invalidate computer...
Ship Power Plant Protected by High Torque Alarm
A ship management company that specializes in the transport of pleasure yachts had developed a new, efficient ship design. One of the features of the vessel was that the power plant was closely matched to the two 5,100 kW electric motors driving the propellers....
MARINE TECHNICAL TOPICS
WHAT IS A MARINE SHAFT POWER METER?
A marine shaft power meter measures the real time torque (torsion), speed, and power of a marine shaft. The meter uses a strain gage to measure torque and a tachometer to measure shaft speed. Power is calculated by combining these two inputs (shaft speed and torque) into a simple equation.
WHAT IS ENGINE THRUST AND HOW IS IT MEASURED?
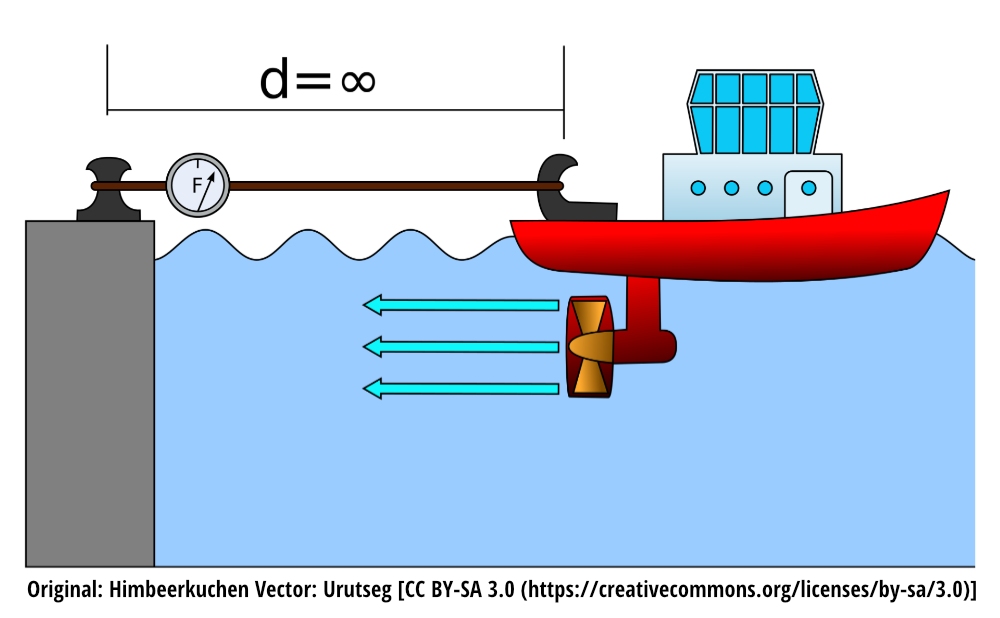
Engine thrust is the axial force exerted by an engine. This is realized as compression on the shaft. The most common way thrust is measured in the marine industry is through the Bollard Pull test. In this test, a boat is tethered to a post, and the engines are brought up to maximum power. A force/tension gage is used in-line with a rope to determine what the maximum Bollard Pull rating (or maximum towing weight) is.
The Bollard Pull test measures the cumulative pull force of all the propellers on a ship. If the thrust value for each of the ships individual engines is desired, then the thrust on each shaft can be measured by using a thrust pattern strain gage. Careful consideration for accuracy should be taken when using this method. Since the compressive displacement of a shaft is much lower than torsional displacement, the strain gage method is not as accurate (typically +/- 10%). An added advantage to using a shaft power meter during Bollard Pull Testing is that the true mechanical horsepower of the engine can be monitored, which can help identify if one engine is underperforming or help root-cause/prevent a failed Bollard Pull test.
WHAT IS HULL FOULING?
Hull fouling is defined as the buildup of organisms (plants, algae, barnacles, etc) on an engine hull. The buildup of these organisms causes the vessel to lose fuel efficiency (due to increased drag on the hull), can lead to the transfer of invasive species, and promotes corrosive damage on the hull. Hull fouling can be discovered by visual inspection or through the use of a shaft power meter. By comparing the output power to a calibrated baseline, ship performance monitoring can help identify if excessive drag is prevalent, which could indicate hull fouling.